 The first feature that comes to mind while writing about the serial number is the serial key we usually use when installing software. Within the same software used by thousands of users, the only way to distinguish a particular user is by his unique identification number. This unique identification number is the serial number, in brief.
The first feature that comes to mind while writing about the serial number is the serial key we usually use when installing software. Within the same software used by thousands of users, the only way to distinguish a particular user is by his unique identification number. This unique identification number is the serial number, in brief.
In one of my SAP implementation projects, the client required a unique identification number for an electronic device that it produces to implement proper tracking for the device's warranty. Depending on the business requirements, these numbers can be implemented at any stage of material flow. This blog is all about the key functionalities and step by step SAP serial number configuration.
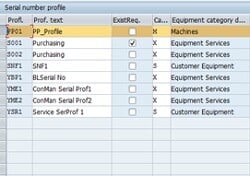
Setting up Serial number profile (Tcode OIS2)
In SAP, serialization can be used at different stages of material flow (inbound, outbound, internal movements, etc.). The serial number has significant use in equipment numbers in SAP Plant Maintenance as well. A Serial Profile is a key that holds this information, and the system acts according to the set up that we configure in the serial profile.
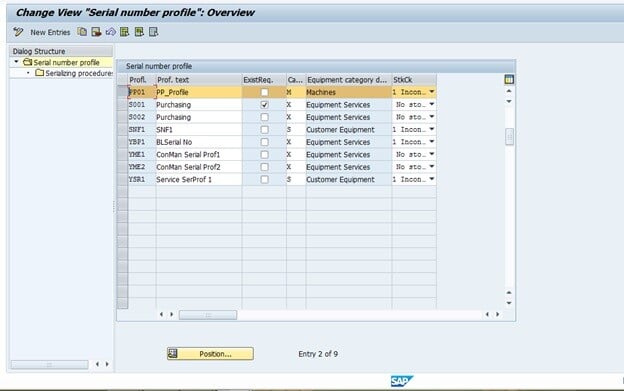
Fig 1: Define Serial Number Profile
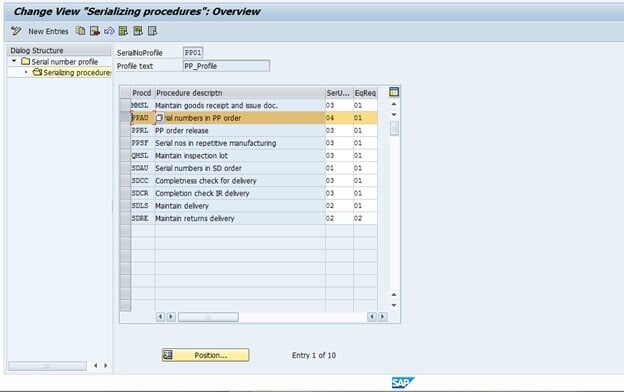
Fig 2: Serializing Procedure
In the serializing procedure (Fig 2), we can see the options whether the serial procedure is relevant to Production Planning (PP), Quality Management (QM), Material Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), or Plant Maintenance (PM) equipment master records. Depending on the business requirement, the required procedures are set in a profile.
This is the main configuration for setting up serialization in SAP. Below we'll see how this serial profile is maintained and used in the transaction.
Serial Profile Maintenance at Material Master
As described, serialization can be used for different stages of a material movement. It is also used in various other SAP modules, so a serial profile needs to be set at the right material number. Once the serial profile configuration is completed, we need to set it in relevant raw material, finish goods or spare parts, etc.
When we set the configured serial profile at a specific material, the system considers this material master record linked with the serialization procedure. Hence, the system will create serial numbers for the materials in relevant SAP transactions.
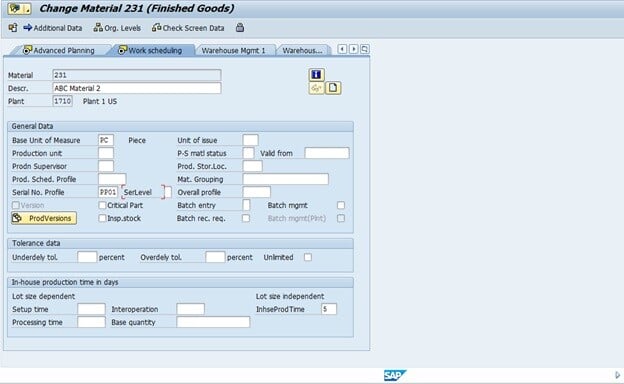
Fig 3: Serial Profile in Material Master
For example, the above serialization procedure in Fig. 3 is for Production Planning (PP), and the finish goods material master is maintained accordingly. We'll see the generated numbers for the production order in the next steps.
Serial Number generation in Production Order
Based on the configuration in the serial profile, the number can be generated during Production Order creation or release. In the example below, we can see the number is assigned for the material that we maintained with a serial number profile.
As the PO quantity was 10, the system generated serial numbers 1 to 10, that means one number for a piece of finished goods. If I create the next Production Order for this material, the system will start from number 11; thus, a unique number will be assigned for a material.
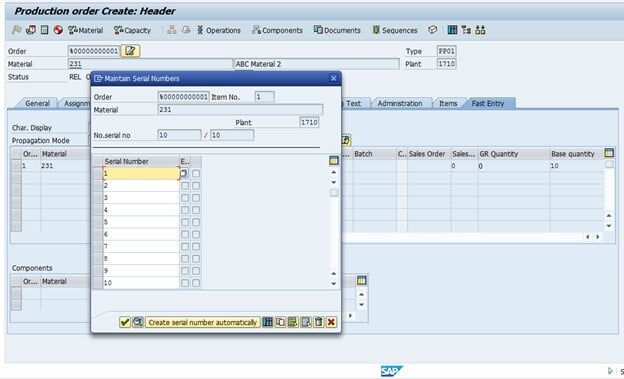
Fig 4: Serial number generation in Production Order
Once the number is generated, we need to perform the subsequent transactions with these numbers accordingly. For example, when we'll perform a goods receipt for this PO, we need to complete it with the number. In the ideal case, the GR should be in the warehouse area with an RF gun. So, physically whatever serial number has arrived at the warehouse for a PO, the barcode should be scanned, and the relevant transactions should be completed.
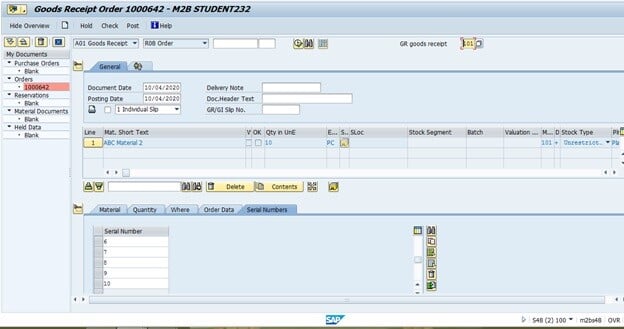
Fig 5: Production Order GR with Serial Number
Serial Number History
A serial number can be checked at any point in time for checking the relevant information. We use SAP transaction code IQ09 to display a number. For example, let's review the numbers that we generated in previous steps:
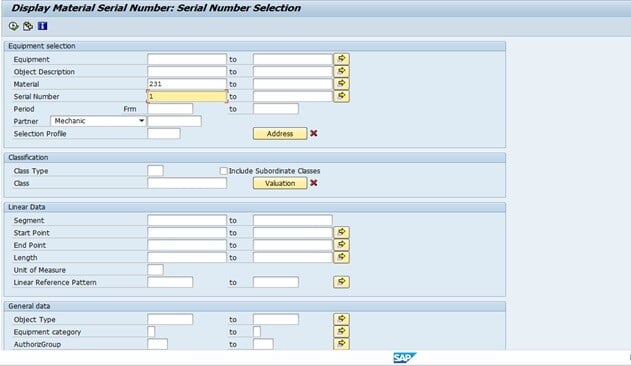
Fig 6: Serial Number display in IQ09 transaction
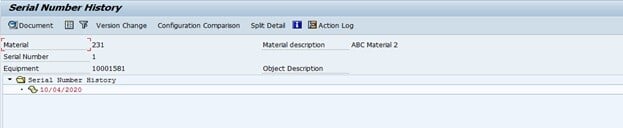
Fig 7: Number History
Fig 8: Number Warranty Tab
Serial Number Logic
Some organizations might have a requirement to implement some specific logic or naming conventions to determine serial numbers. In SAP, the particular logic can be implemented using BAdI.
To summarize, a serial number helps a business to track certain details for specific material. However, keep in mind that it is essential to align the physical process accordingly, as transactions need to be performed with those serial numbers.
Tags:
SAPMar 4, 2021


-1.png)



